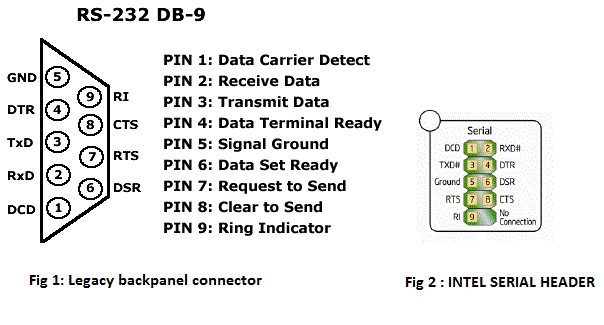
Powered Serial Port Pinout
Posted by admin- in Home -29/09/17
 ULINK2 Users Guide Target Connectors. Home ULINK2 Users Guide. ULINK2 provides five JTAG connectors. They support various cable. The connectors. A narrow 2. ARM. A standard 2. ARM targets,A 1. 6 pin connector for Infineon OCDS JTAG targets,A 1. STMicroelectronics PSD targets. ARM targets Mfgr Don Connex PN. C4. 2 or Samtec PN SHF 1. L D TH. The Samtec part is available with different options for. A cable for each connector is shipped with the ULINK2 Standard. Product. If you must change cables, then make sure to line up the. Pin 1 is. labeled on the board. ULINK2 Adapter Connectors cover off. ULINK2 supports both JTAG and Serial Wire Mode interfaces. Refer. to the appropriate pinout diagram for the ULINK2 adapter connectors. Signal. Connects to. TMSTest Mode State pin Use 1. K Ohm pull up. resistor to VCC. The NanoPi NEOabbreviated as NEO is another fun board developed by FriendlyARM for makers, hobbyists and fans. Hardware Spec. CPU Allwinner H3, Quadcore CortexA7. GPIB, HPIB Bus description, GPI Bus information, timing and General Purpose Interface Bus pin outs, IEEE488 Pinout and a Handshacking diagram to show data transfers. Pinout of Null modem cables and layout of 9 pin DSUB female connector and 25 pin DSUB female connectorDE9 to DE9, DE9 to DE25 cables. Use this cable to connect. Here are the manuals for the 93 to 96 imprezas. Pre 97 Impreza including. TDOTest Data Out pin. RTCKJTAG Return Test Cloc. K. see Note belowTDITest Data In pin Use 1. K Ohm pull up resistor. VCC. TRSTTest Re. Se. T pin Use 1. K Ohm pull up resistor. VCC. TRST is optional and not available on some devices. You. may leave it unconnected.
ULINK2 Users Guide Target Connectors. Home ULINK2 Users Guide. ULINK2 provides five JTAG connectors. They support various cable. The connectors. A narrow 2. ARM. A standard 2. ARM targets,A 1. 6 pin connector for Infineon OCDS JTAG targets,A 1. STMicroelectronics PSD targets. ARM targets Mfgr Don Connex PN. C4. 2 or Samtec PN SHF 1. L D TH. The Samtec part is available with different options for. A cable for each connector is shipped with the ULINK2 Standard. Product. If you must change cables, then make sure to line up the. Pin 1 is. labeled on the board. ULINK2 Adapter Connectors cover off. ULINK2 supports both JTAG and Serial Wire Mode interfaces. Refer. to the appropriate pinout diagram for the ULINK2 adapter connectors. Signal. Connects to. TMSTest Mode State pin Use 1. K Ohm pull up. resistor to VCC. The NanoPi NEOabbreviated as NEO is another fun board developed by FriendlyARM for makers, hobbyists and fans. Hardware Spec. CPU Allwinner H3, Quadcore CortexA7. GPIB, HPIB Bus description, GPI Bus information, timing and General Purpose Interface Bus pin outs, IEEE488 Pinout and a Handshacking diagram to show data transfers. Pinout of Null modem cables and layout of 9 pin DSUB female connector and 25 pin DSUB female connectorDE9 to DE9, DE9 to DE25 cables. Use this cable to connect. Here are the manuals for the 93 to 96 imprezas. Pre 97 Impreza including. TDOTest Data Out pin. RTCKJTAG Return Test Cloc. K. see Note belowTDITest Data In pin Use 1. K Ohm pull up resistor. VCC. TRSTTest Re. Se. T pin Use 1. K Ohm pull up resistor. VCC. TRST is optional and not available on some devices. You. may leave it unconnected.  This is an open collectoropen drain. TCLKTest CLoc. K pin Use 1. K Ohm pull down resistor. GND. VCCPositive Supply Voltage Power supply for JTAG. GNDDigital ground.
This is an open collectoropen drain. TCLKTest CLoc. K pin Use 1. K Ohm pull down resistor. GND. VCCPositive Supply Voltage Power supply for JTAG. GNDDigital ground.  RS232 Connections That WORK Connecting Devices or Converters. USB Connector Pinouts. USB is a serial bus. It uses 4 shielded wires two for power 5v GND and two for differential data signals labelled as D and D in pinout. Updated 25815 to include link to V6 RS232 2. 5mm to 9 pin Dtype pinout Updated 1515 to include notes on Prolific USB to serial adapter You will. RESETRSTIN pin Connect this pin to the active. CPU. This is an. open collectoropen drain output. CPUCLKCPU clock according IEEE Standard 1. OCDSEEnableDisable OCDS interface. Infineon specific. TRAPTrap condition Infineon specific. BRKINHardware break in Infineon specific. BRKOUTHardware break out Infineon specific. JENJTAG Enable STMicroelectronics specific. TSTATJTAG ISP Status STMicroelectronics specific. RSTChip reset STMicroelectronics specific. TERRJTAG ISP Error STMicroelectronics specific. The Serial Wire SW mode is a different operating mode for the. JTAG port where only two pins, TCLK and TMS, are used for the. A third pin can be use optionally to trace data. JTAG. pins and SW pins are shared. TCLK is SWCLK Serial Wire ClockTMS is SWDIO Serial Wire debug Data. InputOutput. TDO is SWO Serial Wire trace OutputSignal. Connects to. SWDIOData IO pin. Use 1. 00. K Ohm pull up resistor to. VCC. SWOOptional trace output pin. SWCLKClock pin. Use 1. K Ohm pull down resistor to. GND. VCCPositive Supply Voltage Power supply for JTAG. GNDDigital ground. RESETRSTIN pin Connect this pin to the active. CPU. This is an. open collectoropen drain output. Additional ARM 1. Samtec 6 Cable Samtec PN FFSD 0. D 0. 6. 0. 0 0. N1. 2 Cable Samtec PN FFSD 0. D 1. 2. 0. 0 0. NNote. ULINK2 is powered through the USB connection. ULINK2 operates at 3. V. All JTAG pins are 5. V. Usually, devices do not include pull up or pull down resistors. JTAG nor SW pins. Resistors should be added externally onto the. However, do not add resistors when the device includes them. Some NXP LPC2. 00. Devices have special pins RTCK. DBGSEL that enable the JTAG interface. For example, on the. NXP LPC2. 12. 9 the signal RTCK must be driven low during RESET. JTAG interface. You may want to add jumpers to your. Related Knowledgebase Articles. USB pinout diagram pinouts. Universal Serial Bus USB is a specification to establish communication between devices and a host controller usually personal computer. Nowdays USB has replaced a variety of earlier PC interfaces such as RS 2. Due to the ability to supply power to the preipheral devices USB is often used as a power charger for portable devices. An USB system architecture consists of a host controller, a USB ports, and multiple connected devices. Additional USB hubs may be included allowing branching into a tree structure with up to five tier levels. USB can connect computer peripherals such as mice, keyboards, digital cameras, PDA, mobile phones, printers, personal media players, flash drives, GPS, Network Adapters, and external hard drives. For many of those devices, USB has become the standard connection method. USB interface aimed to remove the need for adding expansion cards into the computers PCI or PCI Express bus, and improve plug and play capabilities by allowing devices to be hot swapped or added to the system without rebooting the computer. Pin. Name. Cable color. Description. 1VCCRed5 VDC2. D White. Data 3. DGreen. Data 4. GNDBlack. Ground. USB connectors. There are several types of USB connectors. The connector mounted on the host or device is called the receptacle, and the connector attached to the cable is called the plug. The original USB specification detailed Standard A and Standard B plugs and receptacles. Nowdays there are 7 USB connectors known Standard A, Standard B, Mini A, Mini B, Micro A, Micro AB, Micro B. Mini USB pinout and Micro USB pinout are slightly different standard USB uses 4 pins while Mini USB and Micro USB uses 5 pins in connector. The additional pin is used as an attached device presence indicator. USB pinout signals. USB is a serial bus. It uses 4 shielded wires two for power 5v GND and two for differential data signals labelled as D and D in pinout. NRZI Non Return to Zero Invert encoding scheme used to send data with a sync field to synchronise the host and receiver clocks. In USB data cable Data and Data signals are transmitted on a twisted pair. No termination needed. Half duplex differential signaling helps to combat the effects of electromagnetic noise on longer lines. Contrary to popular belief, D and D operate together they are not separate simplex connections. USB 2. 0 provides for a maximum cable length of 5 meters for devices running at Hi Speed. USB transfer modes. Univeral serial bus supports Control, Interrupt, Bulk and Isochronous transfer modes. USB interfaces USB 1. USB 2. 0, USB 3. 0. There are three USB versions known nowdays USB 1. Specifies data rates of 1. Mbits Low Bandwidth, is mostly used for Human Input Devices HID such as keyboards, mouses, joysticks and often the buttons on higher speed devices such as printers or scanners and 1. Mbits Full Bandwidth. USB 2. 0released in 2. USB 1. 0 adds signaling rate of 4. Mbits Hi Speedcompatible with USB 1. USB 2. 0 may not work with USB 1. USB 3. 0released in 2. Gbits Super. SpeedUSB 1. USB 2. 0 shares same connector pinout, USB 3. A USB device must indicate its speed by pulling either the D or D line high to 3. These pull up resistors at the device end will also be used by the host or hub to detect the presence of a device connected to its port. Without a pull up resistor, USB assumes there is nothing connected to the bus. In order to help user to identify maximum speed of device, a USB device often specifies its speed on its cover with one of the USB special marketing logos. When the new device first plugs in, the host enumerates it and loads the device driver necessary to run it. The loading of the appropriate driver is done using a PIDVID Product IDVendor ID combination supplied by attached hardware. The USB host controllers has their own specifications UHCI Universal Host Controller Interface, OHCI Open Host Controller Interface with USB 1. EHCI Enhanced Host Controller Interface is used with USB 2. USB powered devices. The USB connector provides a single 5 volt wire from which connected USB devices may power themselves. A given segment of the bus is specified to deliver up to 5. A. This is often enough to power several devices, although this budget must be shared among all devices downstream of an unpowered hub. A bus powered device may use as much of that power as allowed by the port it is plugged into. Bus powered hubs can continue to distribute the bus provided power to connected devices but the USB specification only allows for a single level of bus powered devices from a bus powered hub. This disallows connection of a bus powered hub to another bus powered hub. Many hubs include external power supplies which will power devices connected through them without taking power from the bus. Devices that need more than 5. A or higher than 5 volts must provide their own power. When USB devices including hubs are first connected they are interrogated by the host controller, which enquires of each their maximum power requirements. However, seems that any load connected to USB port may be treated by operating system as device. The host operating system typically keeps track of the power requirements of the USB network and may warn the computers operator when a given segment requires more power than is available and may shut down devices in order to keep power consumption within the available resource. USB power usage Bus powered hubs Draw Max 1. A at power up and 5. A normally. Self powered hubs Draw Max 1. A, must supply 5. A to each port. Low power, bus powered functions Draw Max 1. A. High power, bus powered functions Self powered hubs Draw Max 1. A, must supply 5. A to each port. Self powered functions Draw Max 1. A. Suspended device Max 0. ADedicated charger mode A simple USB charger should incorporate 2. Ohm resistor between D and D wires sometimes shortcircuit D and D together is enough. The device will then not attempt to transmit or receive data, but can draw up to 1. A, if the supply can provide it. USB voltage Supplied voltage by a host or a powered hub ports is between 4. V and 5. 2. 5 V. Maximum voltage drop for bus powered hubs is 0. V from its host or hub to the hubs output port. All hubs and functions must be able to send configuration data at 4. V, but only low power functions need to be working at this voltage. Normal operational voltage for functions is minimum 4. V. USB cable shielding Shield should only be connected to Ground at the host. No device should connect Shield to Ground. USB cable wires Shielded Data 2. AWG twisted. Power 2. AWG 2. 0 AWG non twisted. Non shielded Data 2. AWG non twisted. Power 2. 8 AWG 2. AWG non twisted. Power Gauge. Max length.
RS232 Connections That WORK Connecting Devices or Converters. USB Connector Pinouts. USB is a serial bus. It uses 4 shielded wires two for power 5v GND and two for differential data signals labelled as D and D in pinout. Updated 25815 to include link to V6 RS232 2. 5mm to 9 pin Dtype pinout Updated 1515 to include notes on Prolific USB to serial adapter You will. RESETRSTIN pin Connect this pin to the active. CPU. This is an. open collectoropen drain output. CPUCLKCPU clock according IEEE Standard 1. OCDSEEnableDisable OCDS interface. Infineon specific. TRAPTrap condition Infineon specific. BRKINHardware break in Infineon specific. BRKOUTHardware break out Infineon specific. JENJTAG Enable STMicroelectronics specific. TSTATJTAG ISP Status STMicroelectronics specific. RSTChip reset STMicroelectronics specific. TERRJTAG ISP Error STMicroelectronics specific. The Serial Wire SW mode is a different operating mode for the. JTAG port where only two pins, TCLK and TMS, are used for the. A third pin can be use optionally to trace data. JTAG. pins and SW pins are shared. TCLK is SWCLK Serial Wire ClockTMS is SWDIO Serial Wire debug Data. InputOutput. TDO is SWO Serial Wire trace OutputSignal. Connects to. SWDIOData IO pin. Use 1. 00. K Ohm pull up resistor to. VCC. SWOOptional trace output pin. SWCLKClock pin. Use 1. K Ohm pull down resistor to. GND. VCCPositive Supply Voltage Power supply for JTAG. GNDDigital ground. RESETRSTIN pin Connect this pin to the active. CPU. This is an. open collectoropen drain output. Additional ARM 1. Samtec 6 Cable Samtec PN FFSD 0. D 0. 6. 0. 0 0. N1. 2 Cable Samtec PN FFSD 0. D 1. 2. 0. 0 0. NNote. ULINK2 is powered through the USB connection. ULINK2 operates at 3. V. All JTAG pins are 5. V. Usually, devices do not include pull up or pull down resistors. JTAG nor SW pins. Resistors should be added externally onto the. However, do not add resistors when the device includes them. Some NXP LPC2. 00. Devices have special pins RTCK. DBGSEL that enable the JTAG interface. For example, on the. NXP LPC2. 12. 9 the signal RTCK must be driven low during RESET. JTAG interface. You may want to add jumpers to your. Related Knowledgebase Articles. USB pinout diagram pinouts. Universal Serial Bus USB is a specification to establish communication between devices and a host controller usually personal computer. Nowdays USB has replaced a variety of earlier PC interfaces such as RS 2. Due to the ability to supply power to the preipheral devices USB is often used as a power charger for portable devices. An USB system architecture consists of a host controller, a USB ports, and multiple connected devices. Additional USB hubs may be included allowing branching into a tree structure with up to five tier levels. USB can connect computer peripherals such as mice, keyboards, digital cameras, PDA, mobile phones, printers, personal media players, flash drives, GPS, Network Adapters, and external hard drives. For many of those devices, USB has become the standard connection method. USB interface aimed to remove the need for adding expansion cards into the computers PCI or PCI Express bus, and improve plug and play capabilities by allowing devices to be hot swapped or added to the system without rebooting the computer. Pin. Name. Cable color. Description. 1VCCRed5 VDC2. D White. Data 3. DGreen. Data 4. GNDBlack. Ground. USB connectors. There are several types of USB connectors. The connector mounted on the host or device is called the receptacle, and the connector attached to the cable is called the plug. The original USB specification detailed Standard A and Standard B plugs and receptacles. Nowdays there are 7 USB connectors known Standard A, Standard B, Mini A, Mini B, Micro A, Micro AB, Micro B. Mini USB pinout and Micro USB pinout are slightly different standard USB uses 4 pins while Mini USB and Micro USB uses 5 pins in connector. The additional pin is used as an attached device presence indicator. USB pinout signals. USB is a serial bus. It uses 4 shielded wires two for power 5v GND and two for differential data signals labelled as D and D in pinout. NRZI Non Return to Zero Invert encoding scheme used to send data with a sync field to synchronise the host and receiver clocks. In USB data cable Data and Data signals are transmitted on a twisted pair. No termination needed. Half duplex differential signaling helps to combat the effects of electromagnetic noise on longer lines. Contrary to popular belief, D and D operate together they are not separate simplex connections. USB 2. 0 provides for a maximum cable length of 5 meters for devices running at Hi Speed. USB transfer modes. Univeral serial bus supports Control, Interrupt, Bulk and Isochronous transfer modes. USB interfaces USB 1. USB 2. 0, USB 3. 0. There are three USB versions known nowdays USB 1. Specifies data rates of 1. Mbits Low Bandwidth, is mostly used for Human Input Devices HID such as keyboards, mouses, joysticks and often the buttons on higher speed devices such as printers or scanners and 1. Mbits Full Bandwidth. USB 2. 0released in 2. USB 1. 0 adds signaling rate of 4. Mbits Hi Speedcompatible with USB 1. USB 2. 0 may not work with USB 1. USB 3. 0released in 2. Gbits Super. SpeedUSB 1. USB 2. 0 shares same connector pinout, USB 3. A USB device must indicate its speed by pulling either the D or D line high to 3. These pull up resistors at the device end will also be used by the host or hub to detect the presence of a device connected to its port. Without a pull up resistor, USB assumes there is nothing connected to the bus. In order to help user to identify maximum speed of device, a USB device often specifies its speed on its cover with one of the USB special marketing logos. When the new device first plugs in, the host enumerates it and loads the device driver necessary to run it. The loading of the appropriate driver is done using a PIDVID Product IDVendor ID combination supplied by attached hardware. The USB host controllers has their own specifications UHCI Universal Host Controller Interface, OHCI Open Host Controller Interface with USB 1. EHCI Enhanced Host Controller Interface is used with USB 2. USB powered devices. The USB connector provides a single 5 volt wire from which connected USB devices may power themselves. A given segment of the bus is specified to deliver up to 5. A. This is often enough to power several devices, although this budget must be shared among all devices downstream of an unpowered hub. A bus powered device may use as much of that power as allowed by the port it is plugged into. Bus powered hubs can continue to distribute the bus provided power to connected devices but the USB specification only allows for a single level of bus powered devices from a bus powered hub. This disallows connection of a bus powered hub to another bus powered hub. Many hubs include external power supplies which will power devices connected through them without taking power from the bus. Devices that need more than 5. A or higher than 5 volts must provide their own power. When USB devices including hubs are first connected they are interrogated by the host controller, which enquires of each their maximum power requirements. However, seems that any load connected to USB port may be treated by operating system as device. The host operating system typically keeps track of the power requirements of the USB network and may warn the computers operator when a given segment requires more power than is available and may shut down devices in order to keep power consumption within the available resource. USB power usage Bus powered hubs Draw Max 1. A at power up and 5. A normally. Self powered hubs Draw Max 1. A, must supply 5. A to each port. Low power, bus powered functions Draw Max 1. A. High power, bus powered functions Self powered hubs Draw Max 1. A, must supply 5. A to each port. Self powered functions Draw Max 1. A. Suspended device Max 0. ADedicated charger mode A simple USB charger should incorporate 2. Ohm resistor between D and D wires sometimes shortcircuit D and D together is enough. The device will then not attempt to transmit or receive data, but can draw up to 1. A, if the supply can provide it. USB voltage Supplied voltage by a host or a powered hub ports is between 4. V and 5. 2. 5 V. Maximum voltage drop for bus powered hubs is 0. V from its host or hub to the hubs output port. All hubs and functions must be able to send configuration data at 4. V, but only low power functions need to be working at this voltage. Normal operational voltage for functions is minimum 4. V. USB cable shielding Shield should only be connected to Ground at the host. No device should connect Shield to Ground. USB cable wires Shielded Data 2. AWG twisted. Power 2. AWG 2. 0 AWG non twisted. Non shielded Data 2. AWG non twisted. Power 2. 8 AWG 2. AWG non twisted. Power Gauge. Max length.